Understanding the Shadow: Navigating Persistent Depressive Disorder
Introduction
In today’s truehearted pace world, mental health struggles are become progressively visible. Among the myriad of mental health conditions, persistent depressive disorder (PDD), likewise know as dysthymia, oftentimes lurk in the shadows. It is a chronic form of depression that can importantly impact one’s quality of life. This article delves into the intricacies of PDD, provide insights, guidance, and real life examples to help those affect and their loved ones navigate this challenging condition.
 Source: firstlightpsych.com
Source: firstlightpsych.com What’s persistent depressive disorder?
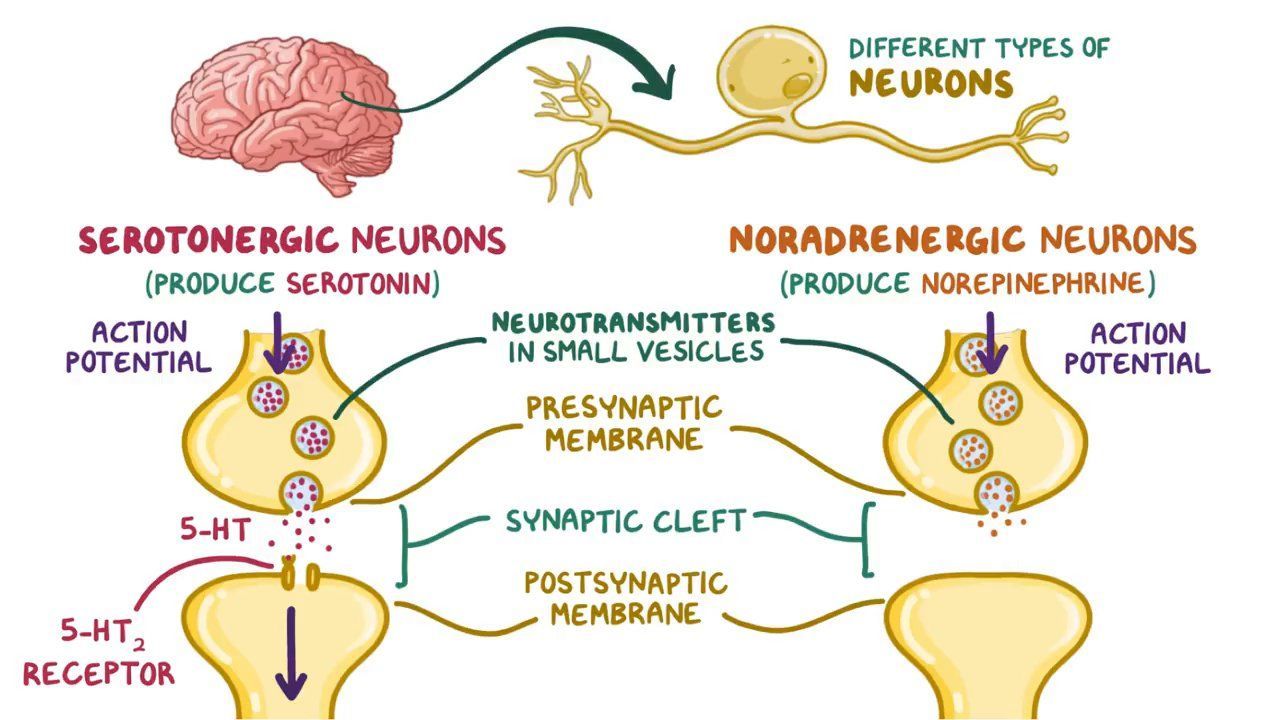
Persistent depressive disorder is a long term form of depression last for astatine least two years. Unlike major depressive disorder, which can occur in episodes, PDD is a continuous, chronic condition. Individuals with PDD frequently experience a low mood on most days, along with other depressive symptoms that can interfere with everyday functioning.
Symptoms of persistent depressive disorder
- Constant feelings of sadness or hopelessness
- Low self-esteem
- Fatigue and low energy
- Difficulty concentrate or make decisions
- Changes in appetite (overeating or poor appetite )
- Sleep disturbances (insomnia or hypersomnia )
- Feelings of inadequacy
- Difficulty overcome challenges
Causes and risk factors
The exact cause of PDD is not full understand, but it’s believe to be a combination of genetic, biological, environmental, and psychological factors. Some potential risk factors include:
- Family history: Have relatives with depression increase the risk.
- Brain chemistry: Imbalances in neurotransmitters may play a role.
- Trauma or stress: Experience traumatic events can trigger PDD.
- Chronic illness: Ongoing health issues can contribute to persistent depression.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnose PDD can be challenge due to its long term nature and overlap with other mood disorders. Healthcare professionals frequently conduct thorough evaluations, include interviews and questionnaires, to assess symptoms.
Treatment options
- Psychotherapy: Cognitive behavioral therapy (cCBT)and interpersonal therapy ( (tIPT)ve provprovedective in manage pddPDD
- Medication: Antidepressants such as SSRIs or SSRIs may be prescribed to help balance brain chemistry.
- Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and adequate sleep can improve mood and overall comfortably being.
- Mindfulness and stress reduction: Practices like meditation and yoga can reduce stress and enhance emotional resilience.
Real life example
Consider the story of Sarah, a 34-year-old marketing executive. For over a decade, Sarah feel an e’er present cloud of sadness, which she attributes to stress. Despite her success at work, shestrugglese with loself-esteemem and constant fatigue. After experience a specially challenging yearSarahah seek help and wadiagnosedse wiPDDpdd. Through a combination of therapy, medication, and lifestyle adjustmentSarahrah gradually find a way to cope with her condition, lead to a more fulfilling life.
 Source: calmsage.com
Source: calmsage.com Live with persistent depressive disorder
Manage PDD is an ongoing process. Here are some tips to help individuals and their families:
- Seek support: Connect with a therapist or support group can provide valuable insights and encouragement.
- Set realistic goals: Break tasks into manageable steps to avoid feel overwhelmed.
- Maintain a routine: Structure can bring stability to your day-to-day life.
- Practice self compassion: Be kind to yourself and acknowledge your efforts.
- Educate loved ones: Help family and friends understand PDD to foster a supportive environment.
Conclusion
Persistent depressive disorder is a challenging condition that require understanding and a multi faceted approach to management. By recognize the symptoms, seek treatment, and implement cope strategies, individuals with PDD can lead meaningful and productive lives. As we continue to learn about mental health, it’s crucial to foster an environment of support and empathy. For further information and resources, consider reach out to mental health professionals or trust organizations dedicate to mental intimately being.